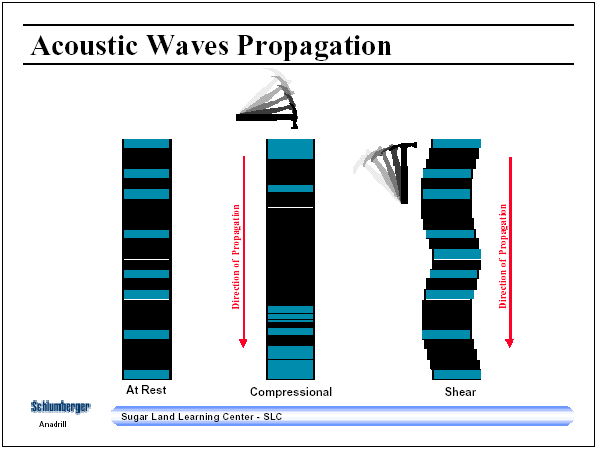
Body waves travel through a medium. The sounds that you hear are examples of body waves in air. Body waves in the earth can be classified into compressional waves in which the direction of particle motion is in the same direction as the wave is propagating, and shear waves in which the direction of particle motion is perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Shear waves can only exist in solids, not in fluids such as air, water or drilling fluids. Shear or S-wave velocity is slower than compressional, or P- wave velocity. A shear wave may have both a horizontal component called an SH waves where the direction of particle motion is in the horizontal plane and a vertical component called SV waves in which the particle motion is in the vertical plane.

Figure 1 - Compressional and shear waves